cell
a small room as in a convent or prison; basic structural unit of all organisms: a one-celled animal
Not to be confused with:
sell – to transfer goods or render services in exchange for money: sell the car
Abused, Confused, & Misused Words by Mary Embree Copyright © 2007, 2013 by Mary Embree
cell
(sĕl)n.
1. A narrow confining room, as in a prison or convent.
2. A small enclosed cavity or space, such as a compartment in a honeycomb or within a plant ovary or an area bordered by veins in an insect's wing.
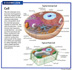
3. Biology The smallest structural unit of an organism that is capable of independent functioning, consisting of cytoplasm, usually one nucleus, and various other organelles, all surrounded by a semipermeable cell membrane.
4. Architecture See web.
5. The smallest organizational unit of a clandestine group or movement, such as a banned political movement or a terrorist group. A cell's leader is often the only person who knows members of the organization outside the cell.
6. Electricity
a. A single unit for electrolysis or conversion of chemical into electric energy, usually consisting of a container with electrodes and an electrolyte; a battery. Also called electrochemical cell.
b. A single unit that converts radiant energy into electric energy: a solar cell.
7. A fuel cell.
8.
a. A geographic area or zone surrounding a transmitter in a cellular telephone system.
b. A cell phone.
9. Computers A basic unit of storage in a computer memory that can hold one unit of information, such as a character or word.
10. A storm cell.
11. A small humble abode, such as a hermit's cave or hut.
12. A small religious house dependent on a larger one, such as a priory within an abbey.
13. A box or other unit on a spreadsheet or similar array at the intersection of a column and a row.
v. celled, cell·ing, cells
v.tr.
To store in a honeycomb.
v.intr.
To live in or share a prison cell.
[Middle English celle, from Old English cell and from Old French, both from Latin cella, chamber; see kel- in Indo-European roots.]
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
cell
(sɛl)n
1. a small simple room, as in a prison, convent, monastery, or asylum; cubicle
2. any small compartment: the cells of a honeycomb.
3. (Biology) biology the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms. It consists of a nucleus, containing the genetic material, surrounded by the cytoplasm in which are mitochondria, lysosomes, ribosomes, and other organelles. All cells are bounded by a cell membrane; plant cells have an outer cell wall in addition
4. (Biology) biology any small cavity or area, such as the cavity containing pollen in an anther
5. (General Physics) a device for converting chemical energy into electrical energy, usually consisting of a container with two electrodes immersed in an electrolyte. See also primary cell, secondary cell, dry cell, wet cell, fuel cell
6. (Chemistry) short for electrolytic cell
7. (Ecclesiastical Terms) a small religious house dependent upon a larger one
8. (Government, Politics & Diplomacy) a small group of persons operating as a nucleus of a larger political, religious, or other organization: Communist cell.
9. (Mathematics) maths a small unit of volume in a mathematical coordinate system
10. (Zoology) zoology one of the areas on an insect wing bounded by veins
11. (Broadcasting) the geographical area served by an individual transmitter in a cellular radio network
[C12: from Medieval Latin cella monk's cell, from Latin: room, storeroom; related to Latin cēlāre to hide]
ˈcell-ˌlike adj
cell
(sɛl)n
(Film) a variant spelling of cel
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
cell
(sɛl)n.
1. a small room, as in a convent or prison.
2. any of various small compartments or bounded areas forming part of a whole.
3. a usu. microscopic structure containing nuclear and cytoplasmic material enclosed by a semipermeable membrane and, in plants, a cell wall; the basic structural unit of all organisms.
4. a small group acting as a unit within a larger organization: a local cell of a political party.
5. a device that converts chemical energy into electricity, usu. consisting of two different kinds of conductors surrounded by an electrolyte; battery.
6. Also called electrolytic cell. a device for producing electrolysis, consisting essentially of the electrolyte, its container, and the electrodes.
7. a monastery or nunnery, dependent on a larger religious house.
8. one of the areas into which the wing of an insect is divided by the veins.
9. locule.
10. one of the separate areas covered by a radio transmitter in a cellular phone system.
[before 1150; Middle English celle (< Old French), Old English cell < Medieval Latin cella monastic cell, Latin: room; see cella]
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
cell
(sĕl)1. The basic unit of living matter in all organisms, consisting of protoplasm enclosed within a cell membrane. All cells except bacterial cells have a distinct nucleus that contains the cell's DNA as well as other structures like mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. The main source of energy for all of the biological processes that take place within a cell is ATP. See more at eukaryote, prokaryote.
2. Any of various devices or units within such devices that are capable of converting some form of energy into electricity. Solar cells convert sunlight into electricity, and car batteries contain cells that convert chemical energy into electricity.
cellular adjective
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
cell
Small group of individuals who work together for clandestine or subversive purposes.
Dictionary of Military and Associated Terms. US Department of Defense 2005.
Cell
a small religious group or community connected to a monastery or convent; a unit of persons forming part of a network in a political party; a communist cell; a cell of workers.Dictionary of Collective Nouns and Group Terms. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
cell
1. The basic unit of all living things.
2. The basic unit of the body. Most cells comprise a nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm within a membrane.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. |  cell - any small compartment; "the cells of a honeycomb" cell - any small compartment; "the cells of a honeycomb"compartment - a space into which an area is subdivided |
| 2. | cell - (biology) the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms; they may exist as independent units of life (as in monads) or may form colonies or tissues as in higher plants and animals animate thing, living thing - a living (or once living) entity organism, being - a living thing that has (or can develop) the ability to act or function independently recombinant - a cell or organism in which genetic recombination has occurred blastomere - any cell resulting from cleavage of a fertilized egg flagellated cell - any cell or one-celled organism equipped with a flagellum fibre, fiber - any of several elongated, threadlike cells (especially a muscle fiber or a nerve fiber) Kupffer's cell - specialized cells in the liver that destroy bacteria, foreign proteins, and worn-out blood cells beta cell - a cell that produces insulin in the isles of Langerhans in the pancreas cell membrane, cytomembrane, plasma membrane - a thin membrane (a double layer of lipids) enclosing the cytoplasm of a cell; proteins in the membrane control passage of ions (like sodium or potassium or calcium) in and out of the cell; "all cells have a cell membrane" somatic cell, vegetative cell - any of the cells of a plant or animal except the reproductive cells; a cell that does not participate in the production of gametes; "somatic cells are produced from preexisting cells"; blastema - a mass of undifferentiated cells from which an organ or body part develops energid, protoplast - a biological unit consisting of a nucleus and the body of cytoplasm with which it interacts fertilized ovum, zygote - (genetics) the diploid cell resulting from the union of a haploid spermatozoon and ovum (including the organism that develops from that cell) parthenote - a cell resulting from parthenogenesis cytol, cytoplasm - the protoplasm of a cell excluding the nucleus; is full of proteins that control cell metabolism cell nucleus, karyon, nucleus - a part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction cell organ, cell organelle, organelle - a specialized part of a cell; analogous to an organ; "the first organelle to be identified was the nucleus" vacuole - a tiny cavity filled with fluid in the cytoplasm of a cell embryonic cell, formative cell - a cell of an embryo germ cell, reproductive cell, sex cell - a spermatozoon or an ovum; a cell responsible for transmitting DNA to the next generation gametocyte - an immature animal or plant cell that develops into a gamete by meiosis polar body - a small cell containing little cytoplasm that is produced along with the oocyte and later discarded Leydig cell, Leydig's cell - a cell in the testes that secretes the hormone testosterone Sertoli cell, Sertoli's cell - elongated cells found in the seminiferous tubules of the testis; apparently they nourish the spermatids biological science, biology - the science that studies living organisms plant cell - a cell that is a structural and functional unit of a plant archespore, archesporium - primitive cell or group of cells from which a mother cell develops daughter cell - a cell formed by the division or budding of another cell; "anthrax grows by dividing into two daughter cells that are generally identical" mother cell - cell from which another cell of an organism (usually of a different sort) develops; "a sperm cell develops from a sperm mother cell" arthrospore - one of a string of thick walled vegetative resting cells formed by some algae and fungi arthrospore - a body that resembles a spore but is not an endospore; produced by some bacteria totipotent - having the ability to give rise to unlike cells; "embryonic stem cells are totipotent" | |
| 3. | 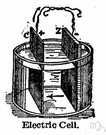 cell - a device that delivers an electric current as the result of a chemical reaction cell - a device that delivers an electric current as the result of a chemical reactionelectrical device - a device that produces or is powered by electricity electrolytic cell - a cell containing an electrolyte in which an applied voltage causes a reaction to occur that would not occur otherwise (such as the breakdown of water into hydrogen and oxygen) fuel cell - cell that produces electricity by oxidation of fuel (hydrogen and oxygen or zinc and air); often used in electric cars photovoltaic cell, solar cell - a cell that converts solar energy into electrical energy secondary cell, storage cell - a cell that can be recharged galvanic cell, primary cell, voltaic cell - an electric cell that generates an electromotive force by an irreversible conversion of chemical to electrical energy; cannot be recharged | |
| 4. | cell - a small unit serving as part of or as the nucleus of a larger political movement sleeper cell - a cell of sleepers; "an al-Qaeda sleeper cell may have used Arizona as its base" radical cell, terrorist cell - a cell of terrorists (usually 3 to 5 members); "to insure operational security the members of adjacent terrorist cells usually don't know each other or the identity of their leadership" political entity, political unit - a unit with political responsibilities political movement - a group of people working together to achieve a political goal | |
| 5. |  cell - a hand-held mobile radiotelephone for use in an area divided into small sections, each with its own short-range transmitter/receiver cell - a hand-held mobile radiotelephone for use in an area divided into small sections, each with its own short-range transmitter/receiverradiophone, radiotelephone, wireless telephone - a telephone that communicates by radio waves rather than along cables | |
| 6. | cell - small room in which a monk or nun lives convent - a religious residence especially for nuns monastery - the residence of a religious community room - an area within a building enclosed by walls and floor and ceiling; "the rooms were very small but they had a nice view" | |
| 7. |  cell - a room where a prisoner is kept cell - a room where a prisoner is kept detention cell, detention centre, bullpen - a large cell where prisoners (people awaiting trial or sentence or refugees or illegal immigrants) are confined together temporarily dungeon - a dark cell (usually underground) where prisoners can be confined guardroom - a cell in which soldiers who are prisoners are confined room - an area within a building enclosed by walls and floor and ceiling; "the rooms were very small but they had a nice view" sweatbox - small or narrow cell |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
cell
noun
Collins Thesaurus of the English Language – Complete and Unabridged 2nd Edition. 2002 © HarperCollins Publishers 1995, 2002
Translations
خَلِيَّةخَلِيَّةٌ كَهْرَبائِيّهخَلِيَّهصَوْمَعَه، ، حُجَيْرَهنَخْروبٌ في خَلِيَّةِ نَحْل
calabóscèllula
buňkacelačlánekkobka
celle
solukammiokännykkäkennoparisto
ćelija
cella
klefifrumahólfrafhlaîa, rafhlöîueiningfangaklefi
細胞
세포
cellula
akutėakytascelėelementaskorytas
kamerašūnacelleelements
bunkacela
celica
cellelement
เซลล์
tế bào
cell
[sel]Collins Spanish Dictionary - Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
cell
[ˈsɛl] n [prisoner] → cellule f
[animal, plant] → cellule f cell biology
(ELECTRICITY, ELECTRONICS) → élément m (de pile)
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007
cell
[sɛl] n (in prison, monastery) → cella (Bio) → cellula (Elec) → elemento (di batteria)dry cell (Chem) → cella a secco
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995
cell
(sel) noun1. a small room (especially in a prison or monastery).
2. a very small piece of the substance of which all living things are made; the smallest unit of living matter. The human body is made up of cells.
3. (the part containing the electrodes in) an electrical battery.
4. one of many small compartments making up a structure. the cells of a honeycomb.
cellular (ˈseljulə) adjective1. consisting of cells. cellular tissue.
2. containing tiny hollow spaces. Foam rubber is a cellular substance.
cellphone nounsee cellular phone.
Kernerman English Multilingual Dictionary © 2006-2013 K Dictionaries Ltd.
cell
→ خَلِيَّة buňka celle Zelle κύτταρο célula solu cellule ćelija cellula 細胞 세포 cel celle komórka célula клетка cell เซลล์ hücre tế bào 细胞Multilingual Translator © HarperCollins Publishers 2009
cell
n. célula, unidad estructural de todo organismo viviente.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
- Telephone & cell phone (US)
Telephone and mobile (UK) - Do you have a cell phone? (US)
Do you have a mobile? (UK) - What's your cell number? (US)
What is the number of your mobile? (UK) - Where can I charge my cell phone? (US)
Where can I charge my mobile phone? (UK)
Collins Multilingual Translator © HarperCollins Publishers 2009
cell
n célula; atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS) células escamosas atípicas de significado indeterminado; B — célula B; brain — célula cerebral; CD4 — célula CD4; cytotoxic T — célula T citotóxica; helper T — célula T auxiliar or colaboradora; natural killer — célula asesina natural; packed red blood cells concentrados de hematíes; unit of packed red blood cells concentrado de hematíes; plasma — célula plasmática; red blood — eritrocito (form), hematíe m (form), glóbulo rojo; stem — célula madre; suppressor T — célula T supresora; T — célula T; transitional — célula transicional; white blood — leucocito (form), glóbulo blancoEnglish-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.