Mes·o·po·ta·mi·a
(mĕs′ə-pə-tā′mē-ə) An ancient region of southwest Asia between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in modern-day Iraq. Probably settled before 5000 bc, the area was the home of numerous early civilizations, including Sumer, Akkad, Babylonia, and Assyria. It declined in importance after Mongol invaders destroyed its extensive irrigation system in ad 1258.
Mes′o·po·ta′mi·an adj. & n.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Mesopotamia
(ˌmɛsəpəˈteɪmɪə)n
(Placename) a region of SW Asia between the lower and middle reaches of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers: site of several ancient civilizations
[Latin from Greek mesopotamia (khora) (the land) between rivers]
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
Mes•o•po•ta•mi•a
(ˌmɛs ə pəˈteɪ mi ə)n.
an ancient region in W Asia between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers: now part of Iraq.
Mes`o•po•ta′mi•an, adj., n.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mesopotamia
- Translates to "area or country between two rivers"—the Tigris and the Euphrates.See also related terms for rivers.
Farlex Trivia Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. | 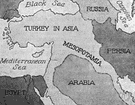 Mesopotamia - the land between the Tigris and Euphrates; site of several ancient civilizations; part of what is now known as Iraq Mesopotamia - the land between the Tigris and Euphrates; site of several ancient civilizations; part of what is now known as IraqAkkadian - an ancient branch of the Semitic languages Assyrian Akkadian, Assyrian - an extinct language of the Assyrians in ancient Mesopotamia Al-Iraq, Irak, Iraq, Republic of Iraq - a republic in the Middle East in western Asia; the ancient civilization of Mesopotamia was in the area now known as Iraq Babylon - the chief city of ancient Mesopotamia and capital of the ancient kingdom of Babylonia Babylonia, Chaldaea, Chaldea - an ancient kingdom in southern Mesopotamia; Babylonia conquered Israel in the 6th century BC and exiled the Jews to Babylon (where Daniel became a counselor to the king) Chaldaea, Chaldea - an ancient region of Mesopotamia lying between the Euphrates delta and the Persian Gulf and the Arabian Desert; settled in 1000 BC and destroyed by the Persians in 539 BC; reached the height of its power under Nebuchadnezzar II Assyria - an ancient kingdom in northern Mesopotamia which is in present-day Iraq Apsu - father of the gods and consort of Tiamat Aruru - mother and earth goddess in Gilgamish epic; identified with Sumerian Ki and Ninkhursag Dagan - god of agriculture and earth; counterpart of Phoenician Dagon Ea - the Babylonian god of wisdom; son of Apsu and father of Marduk; counterpart of the Sumerian Enki; as one of the supreme triad including Anu and Bel he was assigned control of the watery element Namtar, Namtaru - a demon personifying death; messenger of the underworld goddess Ereshkigal bringing death to mankind Nergal - (Akkadian) god ruling with his consort Ereshkigal the world of the dead Ningal - (Akkadian) a goddess; wife of the Moon god Sin Sin - (Akkadian) god of the Moon; counterpart of Sumerian Nanna Tiamat - (Akkadian) mother of the gods and consort of Apsu |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
KahejõemaaMesopotaamia
KaksoisvirranmaaMesopotamia
Mezopotámia
MesopotamienTvåflodslandet
Collins Spanish Dictionary - Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
Mesopotamia
n → Mesopotamien nt
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007