fos·sa 1
(fŏs′ə)n. pl. fos·sae (fŏs′ē′) Anatomy
A small cavity or depression, as in a bone.
[Latin, ditch, from feminine past participle of fodere, to dig.]
fos′sate′ (fŏs′āt′) adj.
fos·sa 2
(fŏs′ə)n.
A catlike carnivorous mammal (Cryptoprocta ferox) of Madagascar, having reddish-brown fur, a long tail, long whiskers, and retractile claws.
[Malagasy fosa.]
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
fossa
(ˈfɒsə)n, pl -sae (-siː)
(Anatomy) an anatomical depression, trench, or hollow area
[C19: from Latin: ditch, from fossus dug up, from fodere to dig up]
fossa
(ˈfɒsə)n
(Animals) a large primitive catlike viverrine mammal, Cryptoprocta ferox, inhabiting the forests of Madagascar: order Carnivora (carnivores). It has thick reddish-brown fur and preys on lemurs, poultry, etc
[from Malagasy]
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
fos•sa1
(ˈfɒs ə)n., pl. fos•sae (ˈfɒs i)
a pit, cavity, or depression, as in a bone.
[1820–30; < Latin: ditch, fosse, short for fossa (terra) dug or dug out (earth), n. use of feminine of fossus, past participle of fodere to dig]
fos•sa2
(ˈfɒs ə)n., pl. -sas.
a large viverrid carnivore, Cryptoprocta ferox, of Madagascar. Also called fos′sa cat`.
[1830–40; < Malagasy]
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
fossa
A shallow depression.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. | 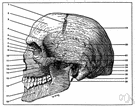 fossa - a concavity in a surface (especially an anatomical depression) fossa - a concavity in a surface (especially an anatomical depression)glenoid cavity, glenoid fossa - the concavity in the head of the scapula that receives the head of the humerus to form the shoulder joint glenoid fossa, mandibular fossa - a deep concavity in the temporal bone at the root of the zygomatic arch that receives the condyle of the mandible epigastric fossa, pit of the stomach - a slight depression in the midline just below the sternum (where a blow can affect the solar plexus) |
| 2. | Fossa - monotypic genus of Madagascar civets closely related to palm civets mammal genus - a genus of mammals fanaloka, Fossa fossa - civet of Madagascar | |
| 3. |  fossa - largest carnivore of Madagascar; intermediate in some respects between cats and civets fossa - largest carnivore of Madagascar; intermediate in some respects between cats and civetsviverrine, viverrine mammal - small cat-like predatory mammals of warmer parts of the Old World |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
fos·sa
n. L. fosa, cavidad, hueco, depresión;
___ glenoid → ___ glenoidea;
___ interpeduncular → ___ interpeduncular;
___ jugular → ___ yugular;
___ mandibular → ___ mandibular;
___ nasal → ___ nasal;
___ navicular → ___ navicular.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
fossa
n fosaEnglish-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.