os·mo·sis
(ŏz-mō′sĭs, ŏs-)n. pl. os·mo·ses (-sēz)
1.
a. Diffusion of fluid through a semipermeable membrane from a solution with a low solute concentration to a solution with a higher solute concentration until there is an equal solute concentration on both sides of the membrane.
b. The tendency of fluids to diffuse in such a manner.
2. A gradual, often unconscious process of assimilation or absorption: learned French by osmosis while residing in Paris for 15 years.
[From obsolete osmose, from earlier endosmose, from French : Greek endo-, endo- + Greek ōsmos, thrust, push (from ōthein, to push).]
os·mot′ic (-mŏt′ĭk) adj.
os·mot′i·cal·ly adv.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
osmosis
(ɒzˈməʊsɪs; ɒs-)n
1. (Biology) the passage of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated to a more concentrated solution until both solutions are of the same concentration
2. (Chemistry) the passage of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated to a more concentrated solution until both solutions are of the same concentration
3. (General Physics) diffusion through any membrane or porous barrier, as in dialysis
4. gradual or unconscious assimilation or adoption, as of ideas
[C19: Latinized form from osmose (n), from Greek ōsmos push, thrust]
osmotic adj
osˈmotically adv
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
os•mo•sis
(ɒzˈmoʊ sɪs, ɒs-)n.
1.
a. the tendency of a fluid, usu. water, to pass through a semipermeable membrane into a solution where the solvent concentration is higher, thus equalizing the concentrations of materials on either side of the membrane.
b. the diffusion of fluids through membranes or porous partitions.
2. a subtle or gradual absorption: to learn by osmosis.
[1865–70; Latinized form of now obsolete osmose osmosis, extracted from endosmose endosmosis < French, =end- end- + Greek ōsm(ós) push, thrust + French -ose -osis]
os•mot′ic (-ˈmɒt ɪk) adj.
os•mot′i•cal•ly, adv.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
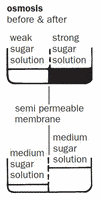
osmosis
left: The concentration of sugar molecules is greater on the right side of the membrane than on the left. The water molecules are small enough to move across the membrane, but the larger sugar molecules cannot pass through.
right: The water molecules move across the membrane until the water and sugar molecules are of equal concentration on both sides. This lowers the water level on the left side and raises it on the right side.
os·mo·sis
(ŏz-mō′sĭs) The movement of a solvent through a membrane separating two solutions of different concentrations. The solvent from the side of weaker concentration usually moves to the side of the stronger concentration, diluting it, until the concentrations of the solutions are equal on both sides of the membrane. ♦ The pressure exerted by the molecules of the solvent on the membrane they pass through is called osmotic pressure. Osmotic pressure is the energy driving osmosis and is important for living organisms because it allows water and nutrients dissolved in water to pass through cell membranes.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
osmosis
the process by which fluids pass through a semipermeable membrane into a solution of lower concentration to equalize the concentration on both sides of the membrane. — osmotic, adj.
See also: Processesthe process by which fluids pass through a semipermeable membrane into a solution of lower concentration to equalize the concentration on both sides of the membrane. — osmotic, adj.
See also: Cells-Ologies & -Isms. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
osmosis
1. Movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane, e.g. a cell membrane.
2. The movement of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a dilute solution to a more concentrated solution.
3. Diffusion of a fluid (e.g., water) through a semipermeable membrane.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. |  osmosis - (biology, chemistry) diffusion of molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration until the concentration on both sides is equal osmosis - (biology, chemistry) diffusion of molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration until the concentration on both sides is equaldialysis - separation of substances in solution by means of their unequal diffusion through semipermeable membranes biological science, biology - the science that studies living organisms chemical science, chemistry - the science of matter; the branch of the natural sciences dealing with the composition of substances and their properties and reactions diffusion - (physics) the process in which there is movement of a substance from an area of high concentration of that substance to an area of lower concentration reverse osmosis - (chemistry) a method of producing pure water; a solvent passes through a semipermeable membrane in a direction opposite to that for natural osmosis when it is subjected to a hydrostatic pressure greater than the osmotic pressure |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
osmóza
Collins Spanish Dictionary - Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
osmosis
n → Osmose f
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995
os·mo·sis
n. osmosis, difusión de un solvente a través de una membrana semipermeable interpuesta entre soluciones de concentración diferente.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
osmosis
n ósmosis fEnglish-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.