an·eu·rysm
also an·eu·rism (ăn′yə-rĭz′əm)n.
An abnormal, blood-filled sac formed by dilation of the wall of a blood vessel or heart ventricle, most commonly the abdominal aorta and intracranial arteries, resulting from disease or trauma to the wall, as in atherosclerosis.
[Middle English aneurisme, ultimately from Greek aneurusma, from aneurein, to dilate : ana-, throughout; see ana- + eurus, wide.]
an′eu·rys′mal (-məl) adj.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
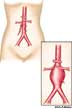
 aneurysmal - relating to or affected by an aneurysm
aneurysmal - relating to or affected by an aneurysm