ax·on
(ăk′sŏn′) also ax·one (-sōn′)n.
The usually long process of a nerve fiber that generally conducts impulses away from the body of the nerve cell.
[Greek axōn, axis.]
ax′on·al (ăk′sə-nəl, ăk-sŏn′əl) adj.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
axon
(ˈæksɒn) oraxone
n
(Biology) the long threadlike extension of a nerve cell that conducts nerve impulses from the cell body. Compare dendrite
[C19: via New Latin from Greek: axis, axle, vertebra]
ˈaxonal, axˈonic adj
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
ax•on
(ˈæk sɒn)n.
the appendage of a neuron that transmits impulses away from the cell body.
[1835–45; < New Latin < Greek áxōn an axle, axis; akin to Latin axis]
ax′on•al (-sə nl, -ˌsɒn l) adj.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
ax·on
(ăk′sŏn′) The long portion of a nerve cell that carries impulses away from the body of the cell. Also called nerve fiber.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
axon
The extension of a neuron, taking impulses away from the cell body.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. | 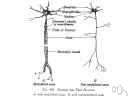 axon - long nerve fiber that conducts away from the cell body of the neuron axon - long nerve fiber that conducts away from the cell body of the neuronnerve fiber, nerve fibre - a threadlike extension of a nerve cell nerve cell, neuron - a cell that is specialized to conduct nerve impulses nerve end, nerve ending - the terminal structure of an axon that does not end at a synapse |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.