Objective: To evaluate the results of 9th rib
costal cartilage in the reconstruction of stage III saddle nose deformity.
(10) He performed wide resection of the abnormal
costal cartilage and sternal isolation, which resulted in a very rigid anterior chest wall.
Among their topics are lower eyelid blepharoplasy techniques, rhinoplasty: reconstruction of the saddle nose deformity using
costal cartilage harvest, closure of septal perforation, techniques for composite grafts in the reconstruction of facial defects, and a percutaneous approach to mandibular angle fractures.
While the auricle (83%) is classically affected most commonly in adults, the larynx and trachea (50%), nasal,
costal cartilage, joints, eye (20-60%), skin (36%), and heart (<%10) are other anatomical structures that can be affected (4).
The age range was limited to 1-45 years so that we did not encounter any problems with evaluation because of calcification in the
costal cartilage.
The incision may be made with less care, leading to muscle or fascial injury,
costal cartilage damage, or muscle denervation.
Zhang et al., "Techniques for improving tragus definition in auricular reconstruction with autogenous
costal cartilage," Journal ofPlastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery, vol.
Axial CT chest demonstrates expansion of the left 9th
costal cartilage with soft tissue thickening on both the inner and outer aspect of the cartilage (Fig.
In cartilage, lipofuscin is deposited in the
costal cartilage [12] and in the nucleus pulposus of degenerated intervertebral discs [11].
Poststernotomy osteomyelitis is a complication of open heart surgery in 1-5% of patients [1] that typically presents as purulent sternocutaneous fistulas and is commonly treated with combined medical and surgical therapy, including antibiotics, partial or total sternectomy, excision of infected
costal cartilage, and chest reconstruction using muscle flaps to fill the chest gap [2].
The material used for graft is autologous cartilage harvested from right 7th
costal cartilage, septal cartilage or ear.
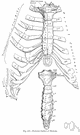 costal cartilage - the cartilages that connect the sternum and the ends of the ribs; its elasticity allows the chest to move in respiration
costal cartilage - the cartilages that connect the sternum and the ends of the ribs; its elasticity allows the chest to move in respiration