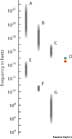
electromagnetic spectrum
electromagnetic spectrum frequencies in hertz
A. gamma rays
B. x-rays
C. ultraviolet rays
D. visible light
E. infrared rays
F. microwaves
G. radio waves
electromagnetic spectrum
n.
The entire range of electromagnetic radiation, which includes, in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength, radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, x-rays, and gamma rays.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
electromagnetic spectrum
n
(General Physics) the complete range of electromagnetic radiation from the longest radio waves (wavelength 105 metres) to the shortest gamma radiation (wavelength 10–13 metre)
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
elec′tromagnet′ic spec′trum
n.
the entire continuous spectrum of all forms of electromagnetic radiation, from gamma rays to long radio waves.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum can be measured in frequencies or in wavelengths. This diagram measures wavelengths in meters, ranging from the longest wavelengths (radio waves) to the shortest (gamma rays). Visible light, which is a band of colors from red to violet, is the only portion of the spectrum that can be seen by the human eye.
electromagnetic spectrum
The entire range of electromagnetic radiation. At one end of the spectrum are gamma rays, which have the shortest wavelengths and high frequencies. At the other end are radio waves, which have the longest wavelengths and low frequencies. Visible light, with intermediate wavelengths and frequencies, is near the center of the spectrum.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
electromagnetic spectrum
The range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation from zero to infinity. It is divided into 26 alphabetically designated bands. See also electronic warfare.
Dictionary of Military and Associated Terms. US Department of Defense 2005.
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. | electromagnetic spectrum - the entire frequency range of electromagnetic waves radio frequency - an electromagnetic wave frequency between audio and infrared extremely low frequency, ELF - below 3 kilohertz very low frequency, VLF - 3 to 30 kilohertz LF, low frequency - 30 to 300 kilohertz medium frequency, MF - 300 to 3000 kilohertz high frequency, HF - 3 to 30 megahertz very high frequency, VHF - 30 to 300 megahertz UHF, ultrahigh frequency - 300 to 3000 megahertz SHF, superhigh frequency - 3 to 30 gigahertz EHF, extremely high frequency - 30 to 300 gigahertz spectrum - an ordered array of the components of an emission or wave actinic radiation, actinic ray - electromagnetic radiation that can produce photochemical reactions gamma radiation, gamma ray - electromagnetic radiation emitted during radioactive decay and having an extremely short wavelength infrared spectrum - the spectrum of infrared radiation light, visible light, visible radiation - (physics) electromagnetic radiation that can produce a visual sensation; "the light was filtered through a soft glass window" line - a single frequency (or very narrow band) of radiation in a spectrum microwave - a short electromagnetic wave (longer than infrared but shorter than radio waves); used for radar and microwave ovens and for transmitting telephone, facsimile, video and data microwave spectrum - the part of the electromagnetic spectrum corresponding to microwaves radio spectrum, radio-frequency spectrum - the entire spectrum of electromagnetic frequencies used for communications; includes frequencies used for radio and radar and television ultraviolet spectrum - the spectrum of ultraviolet radiation color spectrum, visible spectrum - the distribution of colors produced when light is dispersed by a prism |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.