The most commonly injured vessels were the internal iliac artery stem in 6 cases, inferior
gluteal artery in 6 cases, and superior
gluteal artery in 6 cases.
Specific topics include free fibula flap for midface reconstruction, lower eyelid reconstruction with palatal grafts, free flap for hemi-tongue reconstruction, skate flap for nipple reconstruction, hernia repair with open component separation, superior
gluteal artery perforator flap, the medial plantar flap, and pediatric facial reinaimation using a functional gracilis muscle transfer.
Inferior
gluteal artery perforator vessels originate in the inferolateral quadrant [Figure 1].
The branches of the posterior trunk are the superior
gluteal artery, lateral sacral artery, and iliolumbar artery.
Complications with C-clamp placement include superior
gluteal artery and sciatic nerve injury if the spikes are inserted too distally [16,18,19].
After multidisciplinary agreement, the patient underwent urgent Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) that confirmed the three points of bleeding described on CT, that is,
gluteal artery, iliolumbar artery, and lumbar arteries (Figures 2(a) and 2(b)).
The inferior gluteal and first perforator arteries: The tibial portion of the sciatic nerve got arterial supply from the inferior
gluteal artery through its branch, that accompanied the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh (Fig.
At surgery the defect measuring about 16 cm by 24 cm was encountered (Figure 1) An island posterior thigh flap based on the inferior branch of the inferior
gluteal artery was raised (Figures 2, 3, and 4).
Right internal iliac artery ligation was performed below origin of superior
gluteal artery to avoid claudication and hematuria subsided.
The parietal branches secured are the obturator artery, the inferior
gluteal artery and the internal pudendal artery.
Gluteal artery pseudoaneurysm, a rare cause of sciatic pain: case report and literature review.
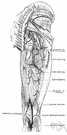 gluteal artery - branches of the internal iliac artery that supply the hip joint and gluteal region
gluteal artery - branches of the internal iliac artery that supply the hip joint and gluteal region