Note: This page may contain content that is offensive or inappropriate for some readers.
mas·toid·i·tis
(măs′toid-ī′tĭs)n.
Inflammation of the mastoid process and mastoid cells.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
mastoiditis
(ˌmæstɔɪˈdaɪtɪs)n
(Pathology) inflammation of the mastoid process
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
mas•toid•i•tis
(ˌmæs tɔɪˈdaɪ tɪs)n.
inflammation of the mastoid process.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. | 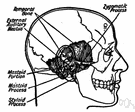 mastoiditis - inflammation of the mastoid mastoiditis - inflammation of the mastoid inflammation, redness, rubor - a response of body tissues to injury or irritation; characterized by pain and swelling and redness and heat |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995
mas·toi·di·tis
n. mastoiditis, infl. de las células mastoideas.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
mastoiditis
n mastoiditis fEnglish-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.