nitrogen cycle
n.
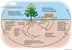
The circulation of nitrogen in nature, consisting of a cycle of chemical reactions in which nitrogen from the atmosphere is fixed in compounds in soil or water, assimilated by plants and animals, released to the soil and water through decomposition, and returned to the atmosphere through denitrification.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
nitrogen cycle
n
(Biology) the natural circulation of nitrogen by living organisms. Nitrates in the soil, derived from dead organic matter by bacterial action, are absorbed and synthesized into complex organic compounds by plants and reduced to nitrates again when the plants and the animals feeding on them die and decay. See nitrification, nitrogen fixation
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
ni′trogen cy`cle
n.
the continuous sequence of natural processes by which nitrogen in the atmosphere and nitrogenous compounds in the soil are converted, as by nitrification and nitrogen fixation, into substances that can be utilized by green plants and then returned to the air and soil as a result of denitrification and plant decay.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
nitrogen cycle
The continuous process by which nitrogen is exchanged between organisms and the environment. Some of the atmosphere's free nitrogen combines with other elements to form compounds that are deposited in the soil. These are then converted by bacteria, in a process called nitrification, into nutrients that are absorbed by the roots of green plants. Nitrogen is then passed into the food chain and returned to the soil by the metabolism and decay of plants and animals.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
nitrogen cycle
The natural circulation of nitrogen (including nitrogen compounds) from air to consuming organisms (plants, animals and bacteria) and back to air.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. |  nitrogen cycle - the circulation of nitrogen; nitrates from the soil are absorbed by plants which are eaten by animals that die and decay returning the nitrogen back to the soil nitrogen cycle - the circulation of nitrogen; nitrates from the soil are absorbed by plants which are eaten by animals that die and decay returning the nitrogen back to the soilbiological process, organic process - a process occurring in living organisms |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.