pleu·ra 1
(plo͝or′ə)n. pl. pleu·rae (plo͝or′ē)
A thin serous membrane in mammals that envelops each lung and folds back to make a lining for the chest cavity.
[Middle English, from Medieval Latin, from Greek, side, rib.]
pleu′ral adj.
pleu·ra 2
(plo͝or′ə)n.
Plural of pleuron.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
pleura
(ˈplʊərə)n, pl pleurae (ˈplʊəriː)
1. (Anatomy) the thin transparent serous membrane enveloping the lungs and lining the walls of the thoracic cavity
2. (Zoology) the plural of pleuron
[C17: via Medieval Latin from Greek: side, rib]
ˈpleural adj
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
pleu•ra
(ˈplʊər ə)n., pl. pleu•rae (ˈplʊər i) .
one of a pair of serous membranes each of which covers a lung and folds back to line the corresponding side of the chest wall.
[1655–65; < New Latin < Greek pleurá (singular) side, rib]
pleu′ral, adj.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
pleu·ra
(plo͝or′ə) A membrane that encloses each lung and lines the chest cavity.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
pleura
The double membrane that covers the lungs and lines the chest wall.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. | 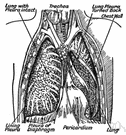 pleura - the thin serous membrane around the lungs and inner walls of the chest pleura - the thin serous membrane around the lungs and inner walls of the chestparietal pleura - pleura that lines the inner chest walls and covers the diaphragm visceral pleura - pleura that covers the lungs pleural cavity - the cavity in the thorax that contains the lungs and heart serosa, serous membrane - a thin membrane lining the closed cavities of the body; has two layers with a space between that is filled with serous fluid |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.