RNA
(är′ĕn-ā′)n.
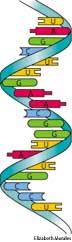
A nucleic acid present in all living cells and many viruses, consisting of a long, usually single-stranded chain of alternating phosphate and ribose units, with one of the bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, or uracil bonded to each ribose molecule. RNA molecules are involved in protein synthesis and sometimes in the transmission of genetic information. Also called ribonucleic acid.
[r(ibo)n(ucleic) a(cid).]
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
RNA
n
(Biochemistry) biochem ribonucleic acid; any of a group of nucleic acids, present in all living cells, that play an essential role in the synthesis of proteins. On hydrolysis they yield the pentose sugar ribose, the purine bases adenine and guanine, the pyrimidine bases cytosine and uracil, and phosphoric acid. See also messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomal RNA, DNA
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
RNA
ribonucleic acid: any of a class of single-stranded nucleic acid molecules of ribose and uracil, found chiefly in the cytoplasm of cells and in certain viruses; important in protein synthesis and in the transmission of genetic information transcribed from DNA. Compare messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA.
[1945–50]
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
RNA
(är′ĕn-ā′) Short for ribonucleic acid. The nucleic acid that determines protein synthesis in all living cells and the genetic makeup of many viruses. RNA consists of a single strand of nucleotides in a variety of lengths and shapes and is mainly produced in the cell nucleus. ♦ Messenger RNA is RNA that carries genetic information from the cell nucleus to the structures in the cytoplasm (known as ribosomes) where protein synthesis takes place. ♦ Transfer RNA is RNA that delivers the amino acids necessary for protein synthesis to the ribosomes. Compare DNA.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
RNA
ribonucleic acid.
See also: Heredity-Ologies & -Isms. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. | RNA - (biochemistry) a long linear polymer of nucleotides found in the nucleus but mainly in the cytoplasm of a cell where it is associated with microsomes; it transmits genetic information from DNA to the cytoplasm and controls certain chemical processes in the cell; "ribonucleic acid is the genetic material of some viruses" biochemistry - the organic chemistry of compounds and processes occurring in organisms; the effort to understand biology within the context of chemistry ribose - a pentose sugar important as a component of ribonucleic acid adenine, A - (biochemistry) purine base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with thymine in DNA and with uracil in RNA informational RNA, messenger RNA, mRNA, template RNA - the template for protein synthesis; the form of RNA that carries information from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome sites of protein synthesis in the cell nRNA, nuclear RNA - ribonucleic acid found in the nucleolus of the cell acceptor RNA, soluble RNA, transfer RNA, tRNA - RNA molecules present in the cell (in at least 20 varieties, each variety capable of combining with a specific amino acid) that attach the correct amino acid to the protein chain that is being synthesized at the ribosome of the cell (according to directions coded in the mRNA) nucleic acid - (biochemistry) any of various macromolecules composed of nucleotide chains that are vital constituents of all living cells polymer - a naturally occurring or synthetic compound consisting of large molecules made up of a linked series of repeated simple monomers |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
рибонуклеинова киселинаРНК
ribonukleiinihappoRNA
RNS
RKS
ribonukleīnskābeRNS
ARN
ribonukleová kyselinaRNK
RNA
N ABBR =ribonucleic acid → ARN mCollins Spanish Dictionary - Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995
RNA
V. ribonucleic acid.English-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.