term
(tûrm)n.
1. A limited or established period of time that something is supposed to last, as a school or court session, tenure in public office, or a prison sentence.
2.
a. A point in time at which something ends; termination: an apprenticeship nearing its term.
b. The end of a normal gestation period: carried the fetus to term.
c. A deadline, as for making a payment.
3. Law
a. A fixed period of time for which an estate is granted.
b. An estate granted for a fixed period.
4.
a. A word or group of words having a particular meaning, especially in a specific field: I was baffled by the technical terms that the programmers were using.
b. terms Language of a certain kind; chosen words: spoke in rather vague terms; praised him in glowing terms.
5. often terms One of the elements of a proposed or concluded agreement; a condition: offered favorable peace terms; one of the terms of the lease; the terms of a divorce settlement.
6. terms The relationship between two people or groups; personal footing: on good terms with her in-laws.
7. Mathematics
a. One of the quantities composing a ratio or fraction or forming a series.
b. One of the quantities connected by addition or subtraction signs in an equation; a member.
8. Logic Each of the two concepts being compared or related in a proposition.
9.
a. A stone or post marking a boundary, especially a squared and downward-tapering pillar adorned with a head and upper torso.
b. An architectural or decorative motif resembling such a marker.
tr.v. termed, term·ing, terms
Idiom: To designate; call.
in terms of
1. As measured or indicated by; in units of: distances expressed in terms of kilometers as well as miles; cheap entertainment, but costly in terms of time wasted.
2. In relation to; with reference to: "narcissistic parents who ... interpret their child's experience entirely in terms of their own history" (Richard Weissbourd).
[Middle English terme, from Old French, from Latin terminus, boundary. N., senses 4-8, from Middle English, from Medieval Latin terminus, from Late Latin, mathematical or logical term, from Latin, boundary, limit.]
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
term
(tɜːm)n
1. a name, expression, or word used for some particular thing, esp in a specialized field of knowledge: a medical term.
2. any word or expression
3. a limited period of time: his second term of office; a prison term.
4. (Education) any of the divisions of the academic year during which a school, college, etc, is in session
5. a point in time determined for an event or for the end of a period
6. (Gynaecology & Obstetrics) Also called: full term the period at which childbirth is imminent
7. (Law) law
a. an estate or interest in land limited to run for a specified period: a term of years.
b. the duration of an estate, etc
c. (formerly) a period of time during which sessions of courts of law were held
d. time allowed to a debtor to settle
8. (Mathematics) maths either of the expressions the ratio of which is a fraction or proportion, any of the separate elements of a sequence, or any of the individual addends of a polynomial or series
9. (Logic) logic
a. the word or phrase that forms either the subject or predicate of a proposition
b. a name or variable, as opposed to a predicate
c. one of the relata of a relation
d. any of the three subjects or predicates occurring in a syllogism
10. (Architecture) architect Also called: terminal, terminus or terminal figure a sculptured post, esp one in the form of an armless bust or an animal on the top of a square pillar
11. (Australian Rules Football) Australian rules football the usual word for quarter10
12. archaic a boundary or limit
vb
(tr) to designate; call: he was termed a thief.
[C13: from Old French terme, from Latin terminus end]
ˈtermly adv
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
term
(tɜrm)n.
1. a word or group of words designating something, esp. in a particular field: the term atom in physics.
2. any word or group of words considered as a member of a construction or utterance.
3. the time or period through which something lasts.
4. a period of time to which limits have been set: a one-year term of office.
5. one of two or more divisions of a school year.
6. an appointed or set time or date, as for the payment of rent, interest, etc.
7. terms,
a. conditions with regard to payment, price, rates, etc.: reasonable terms.
b. conditions or stipulations limiting what is proposed to be granted or done: the terms of a treaty.
c. footing or standing; relations: on good terms with someone.
8. each of the members of which a mathematical expression, a series of quantities, or the like, is composed.
9. (in logic)
a. the subject or predicate of a categorical proposition.
b. the word or expression denoting such a subject or predicate.
10. a herm.
11. Law.
a. an estate, property, etc., to be enjoyed for a specified period.
b. the duration of such a period.
c. the period when a court is in session.
12. completion of pregnancy.
v.t. 13. to apply a particular term or name to; designate.
Idioms: 1. bring to terms, to force to agree to stated demands or conditions.
2. come to terms, to reach an agreement.
3. in terms of, with regard to; concerning.
[1175–1225; Middle English terme < Old French < Latin terminus boundary, limit, end; akin to Greek térmōn limit]
term.
1. terminal.
2. termination.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
term
(tûrm) Mathematics
1. Each of the quantities or expressions that form the parts of a ratio or the numerator and denominator of a fraction.
2. Any of the quantities in an equation that are connected to other quantities by a plus sign or a minus sign.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
term
– semester – quarter1. 'term'
At a British school, each year is divided into three terms. At an American school, it is divided into four terms.
...the summer term.
2. 'semester'
At a British college or university, each year is also divided into three terms.
At an American college or university, it is divided into two semesters, three trimesters, or four quarters.
The first semester starts in three weeks.
Collins COBUILD English Usage © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 2004, 2011, 2012
term
Past participle: termed
Gerund: terming
| Imperative |
|---|
| term |
| term |
Collins English Verb Tables © HarperCollins Publishers 2011
term
(academic) trimester or semester
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. | term - a word or expression used for some particular thing; "he learned many medical terms" word - a unit of language that native speakers can identify; "words are the blocks from which sentences are made"; "he hardly said ten words all morning" referent - something that refers; a term that refers to another term |
| 2. | term - a limited period of time; "a prison term"; "he left school before the end of term" period, period of time, time period - an amount of time; "a time period of 30 years"; "hastened the period of time of his recovery"; "Picasso's blue period" prison term, sentence, time - the period of time a prisoner is imprisoned; "he served a prison term of 15 months"; "his sentence was 5 to 10 years"; "he is doing time in the county jail" academic session, academic term, school term, session - the time during which a school holds classes; "they had to shorten the school term" midterm - middle of an academic term or a political term in office | |
| 3. | term - (usually plural) a statement of what is required as part of an agreement; "the contract set out the conditions of the lease"; "the terms of the treaty were generous" plural, plural form - the form of a word that is used to denote more than one statement - a message that is stated or declared; a communication (oral or written) setting forth particulars or facts etc; "according to his statement he was in London on that day" agreement, understanding - the statement (oral or written) of an exchange of promises; "they had an agreement that they would not interfere in each other's business"; "there was an understanding between management and the workers" | |
| 4. | term - any distinct quantity contained in a polynomial; "the general term of an algebraic equation of the n-th degree" quantity - the concept that something has a magnitude and can be represented in mathematical expressions by a constant or a variable | |
| 5. | term - one of the substantive phrases in a logical proposition; "the major term of a syllogism must occur twice" subject - (logic) the first term of a proposition grammatical constituent, constituent - (grammar) a word or phrase or clause forming part of a larger grammatical construction predicate - (logic) what is predicated of the subject of a proposition; the second term in a proposition is predicated of the first term by means of the copula; "`Socrates is a man' predicates manhood of Socrates" referent - the first term in a proposition; the term to which other terms relate relatum - a term in a proposition that is related to the referent of the proposition proposition - (logic) a statement that affirms or denies something and is either true or false categorem, categoreme - a categorematic expression; a term capable of standing alone as the subject or predicate of a logical proposition; "names are called categorems" major term - the term in a syllogism that is the predicate of the conclusion minor term - the term in a syllogism that is the subject of the conclusion middle term - the term in a syllogism that is common to both premises and excluded from the conclusion | |
| 6. | term - the end of gestation or point at which birth is imminent; "a healthy baby born at full term" point in time, point - an instant of time; "at that point I had to leave" gestation, gestation period - the period during which an embryo develops (about 266 days in humans) | |
| 7. | 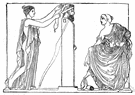 term - (architecture) a statue or a human bust or an animal carved out of the top of a square pillar; originally used as a boundary marker in ancient Rome term - (architecture) a statue or a human bust or an animal carved out of the top of a square pillar; originally used as a boundary marker in ancient Romestatue - a sculpture representing a human or animal architecture - the discipline dealing with the principles of design and construction and ornamentation of fine buildings; "architecture and eloquence are mixed arts whose end is sometimes beauty and sometimes use" | |
| Verb | 1. | term - name formally or designate with a term |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
term
noun
1. word, name, expression, title, label, phrase, denomination, designation, appellation, locution What's the medical term for a heart attack?
3. period, time, spell, while, season, space, interval, span, duration, incumbency a 12 month term of service
4. conclusion, end, close, finish, culmination, fruition Older women are just as capable of carrying a baby to term.
plural noun
1. language, terminology, phraseology, manner of speaking The video explains in simple terms how the tax works.
2. conditions, particulars, provisions, provisos, stipulations, qualifications, premises (Law), specifications the terms of the Helsinki agreement
verb
1. call, name, label, style, entitle, tag, dub, designate, describe as, denominate He had been termed a temporary employee.
come to terms come to an agreement, reach agreement, come to an understanding, conclude agreement Even if they came to terms, investors would object to the merger.
come to terms with something learn to live with, come to accept, be reconciled to, reach acceptance of She had come to terms with the fact that she would always be ill.
in terms of with regard to, concerning, regarding, as to, in connection with, in respect of, as regards, with reference to, in the matter of Our goods compete well in terms of quality and reliability.
Usage: Many people object to the use of in terms of as an all-purpose preposition replacing phrases such as `as regards', `about', and so forth in a context such as the following: in terms of trends in smoking habits, there is good news. They would maintain that in strict usage it should be used to specify a relationship, as in: obesity is defined in terms of body mass index, which involves a bit of cumbersome maths. Nevertheless, despite objections, it is very commonly used as a link word, particularly in speech.
Collins Thesaurus of the English Language – Complete and Unabridged 2nd Edition. 2002 © HarperCollins Publishers 1995, 2002
term
noun1. A limited or specific period of time during which something happens, lasts, or extends:
2. The period during which someone or something exists:
3. A specific length of time characterized by the occurrence of certain conditions or events:
4. A sound or combination of sounds that symbolizes and communicates a meaning:
5. A restricting or modifying element.Often used in plural:
Informal: string (often used in plural).
The American Heritage® Roget's Thesaurus. Copyright © 2013, 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Translations
إصْطِلاحتَعْبِيرفَصْل دِراسيفَصْلٌ دِرَاسِيّ
termíntrimestrúdobívýrazlhůta
betegnelsesemestertidfagudtrykperiode
liidetavmõistepoolaastasuhetermin
lukukausitermiehto
kvartalodnospolugodištetermintromjesečje
félévszemeszterviszonyfeltételfutamidõ
afmarkaî tímabilfræîiheiti, fagorînámsönn
学期用語
용어학기
terminasvadintisįkainiailaiko tarpasmokėjimo sąlygos
dēvētlaika periodsnosauktsemestristermins
termín
izrazmandatpogojisemester
terminvillkorfotterm
ภาคเรียนระยะเวลาที่กำหนด
học kỳthuật ngữ
term
[tɜːm]A. N
1. (= period) → periodo m, período m; (as President, governor, mayor) → mandato m
in the long term → a largo plazo
in the longer term → a un plazo más largo
in the medium term → a medio plazo
during his term of office → bajo su mandato
we have been elected for a three-year term (of office) → hemos sido elegidos para un periodo legislativo de tres años
he will not seek a third term (of office) as mayor → no irá a por un tercer mandato de alcalde, no renovará por tercera vez su candidatura como alcalde
he is currently serving a seven-year prison term → actualmente está cumpliendo una condena de siete años
he served two terms as governor → ocupó el cargo de gobernador durante dos periodos de mandato
in the short term → a corto plazo
despite problems, she carried the baby to term → a pesar de los problemas llevó el embarazo a término
in the long term → a largo plazo
in the longer term → a un plazo más largo
in the medium term → a medio plazo
during his term of office → bajo su mandato
we have been elected for a three-year term (of office) → hemos sido elegidos para un periodo legislativo de tres años
he will not seek a third term (of office) as mayor → no irá a por un tercer mandato de alcalde, no renovará por tercera vez su candidatura como alcalde
he is currently serving a seven-year prison term → actualmente está cumpliendo una condena de siete años
he served two terms as governor → ocupó el cargo de gobernador durante dos periodos de mandato
in the short term → a corto plazo
despite problems, she carried the baby to term → a pesar de los problemas llevó el embarazo a término
2. (Educ) → trimestre m
in the autumn or > fall/spring/summer term (US) → en el primer/segundo/tercer trimestre
they don't like you to take holidays during term → no les gusta que se tomen vacaciones durante el trimestre or en época de clases
in the autumn or > fall/spring/summer term (US) → en el primer/segundo/tercer trimestre
they don't like you to take holidays during term → no les gusta que se tomen vacaciones durante el trimestre or en época de clases
3. (Comm, Jur, Fin) (= period of validity) → plazo m
the policy is near the end of its term → el plazo de la póliza está a punto de vencer
interest rates change over the term of the loan → los tipos de interés cambian a lo largo del plazo del préstamo
the policy is near the end of its term → el plazo de la póliza está a punto de vencer
interest rates change over the term of the loan → los tipos de interés cambian a lo largo del plazo del préstamo
4. (= word) → término m
what do you understand by the term "radical"? → ¿qué entiende usted por (el término) "radical"?
explain it in terms a child might understand → explícalo de manera que un niño lo pueda entender
legal/medical terms → términos mpl legales/médicos
a term of abuse → un término ofensivo, un insulto
a term of endearment → un apelativo cariñoso
he spoke of it only in general terms → sólo habló de ello en términos generales
he spoke of her in glowing terms → habló de ella en términos muy elogiosos
in simple terms → de forma sencilla
she condemned the attacks in the strongest terms → condenó los ataques de la forma más enérgica
technical term → tecnicismo m, término m técnico
see also contradiction, uncertain
what do you understand by the term "radical"? → ¿qué entiende usted por (el término) "radical"?
explain it in terms a child might understand → explícalo de manera que un niño lo pueda entender
legal/medical terms → términos mpl legales/médicos
a term of abuse → un término ofensivo, un insulto
a term of endearment → un apelativo cariñoso
he spoke of it only in general terms → sólo habló de ello en términos generales
he spoke of her in glowing terms → habló de ella en términos muy elogiosos
in simple terms → de forma sencilla
she condemned the attacks in the strongest terms → condenó los ataques de la forma más enérgica
technical term → tecnicismo m, término m técnico
see also contradiction, uncertain
5. (Math, Logic) → término m
6. terms
6.1. (= conditions) → condiciones fpl, términos mpl
according to the terms of the contract → según las condiciones or los términos del contrato
to dictate terms (to sb) → poner condiciones (a algn)
we offer easy terms → ofrecemos facilidades de pago
terms of employment → condiciones fpl de empleo
to compete on equal terms → competir en igualdad de condiciones or en pie de igualdad
they accepted him on his own terms → lo aceptaron con las condiciones que él había puesto
terms of reference (= brief) [of committee, inquiry] → cometido m, instrucciones fpl; [of study] → ámbito m; (= area of responsibility) → responsabilidades fpl, competencia f; (= common understanding) → puntos mpl de referencia
terms of sale → condiciones fpl de venta
terms of trade → condiciones fpl de transacción
to come to terms with sth → asumir or asimilar algo
according to the terms of the contract → según las condiciones or los términos del contrato
to dictate terms (to sb) → poner condiciones (a algn)
we offer easy terms → ofrecemos facilidades de pago
terms of employment → condiciones fpl de empleo
to compete on equal terms → competir en igualdad de condiciones or en pie de igualdad
they accepted him on his own terms → lo aceptaron con las condiciones que él había puesto
terms of reference (= brief) [of committee, inquiry] → cometido m, instrucciones fpl; [of study] → ámbito m; (= area of responsibility) → responsabilidades fpl, competencia f; (= common understanding) → puntos mpl de referencia
terms of sale → condiciones fpl de venta
terms of trade → condiciones fpl de transacción
to come to terms with sth → asumir or asimilar algo
6.2. (= relations)
to be on bad terms with sb → llevarse mal con algn, no tener buenas relaciones con algn
we're on first name terms with all the staff → nos tuteamos con todos los empleados
she is still on friendly terms with him → todavía mantiene una relación amistosa con él
to be on good terms with sb → llevarse bien con algn, tener buenas relaciones con algn
they have managed to remain on good terms → se las arreglaron para quedar bien
we're not on speaking terms at the moment → actualmente no nos hablamos
to be on bad terms with sb → llevarse mal con algn, no tener buenas relaciones con algn
we're on first name terms with all the staff → nos tuteamos con todos los empleados
she is still on friendly terms with him → todavía mantiene una relación amistosa con él
to be on good terms with sb → llevarse bien con algn, tener buenas relaciones con algn
they have managed to remain on good terms → se las arreglaron para quedar bien
we're not on speaking terms at the moment → actualmente no nos hablamos
6.3. (= sense) in terms of: in terms of production we are doing well → en cuanto a la producción vamos bien, por lo que se refiere or por lo que respecta a la producción vamos bien
he never describes women in terms of their personalities → nunca describe a las mujeres refiriéndose a su personalidad
he was talking in terms of buying it → hablaba como si fuera a comprarlo
in economic/political terms → desde el punto de vista económico/político, en términos económicos/políticos
in practical terms this means that → en la práctica esto significa que ...
in real terms incomes have fallen → en términos reales los ingresos han bajado
seen in terms of its environmental impact, the project is a disaster → desde el punto de vista de su impacto en el medio ambiente, el proyecto es un desastre
we were thinking more in terms of an au pair → nuestra idea era más una au pair, teníamos en mente a una au pair
he never describes women in terms of their personalities → nunca describe a las mujeres refiriéndose a su personalidad
he was talking in terms of buying it → hablaba como si fuera a comprarlo
in economic/political terms → desde el punto de vista económico/político, en términos económicos/políticos
in practical terms this means that → en la práctica esto significa que ...
in real terms incomes have fallen → en términos reales los ingresos han bajado
seen in terms of its environmental impact, the project is a disaster → desde el punto de vista de su impacto en el medio ambiente, el proyecto es un desastre
we were thinking more in terms of an au pair → nuestra idea era más una au pair, teníamos en mente a una au pair
B. VT (= designate) → calificar de
he was termed a thief → lo calificaron de ladrón
he termed the war a humanitarian nightmare → calificó la guerra de pesadilla humanitaria
I was what you might term a gangster → yo era lo que se podría llamar un gángster
the problems of what is now termed "the mixed economy" → los problemas de lo que ahora se da en llamar "la economía mixta"
he was termed a thief → lo calificaron de ladrón
he termed the war a humanitarian nightmare → calificó la guerra de pesadilla humanitaria
I was what you might term a gangster → yo era lo que se podría llamar un gángster
the problems of what is now termed "the mixed economy" → los problemas de lo que ahora se da en llamar "la economía mixta"
Collins Spanish Dictionary - Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
term
[ˈtɜːrm] n
(in school, university) → trimestre m
(= period of time) → période f
term of office → mandat m
He lived in New York throughout his term of office → Il a vécu à New York tout au long de son mandat.
Baldwin's second term of office as Premier → le second mandat de Baldwin en tant que premier ministre
term of imprisonment, prison term → peine f de prison
in the short term → à court terme short-term
in the long term → à long terme long-term
in the medium term → à moyen terme medium-term
term of office → mandat m
He lived in New York throughout his term of office → Il a vécu à New York tout au long de son mandat.
Baldwin's second term of office as Premier → le second mandat de Baldwin en tant que premier ministre
term of imprisonment, prison term → peine f de prison
in the short term → à court terme short-term
in the long term → à long terme long-term
in the medium term → à moyen terme medium-term
vt
to term sth sth → appeler qch qch
to term sth sth → appeler qch qch
terms npl
(= conditions) [contract] → termes mpl; [agreement, treaty] → termes mpl, conditions fpl
(COMMERCE) "easy terms" → "facilités de paiement"
to sell sth on easy terms → vendre qch en proposant des facilités de paiement
to sell sth on easy terms → vendre qch en proposant des facilités de paiement
[relationship] → termes mpl
to be on good terms with sb → être en bons termes avec qn
We parted on good terms → Nous nous sommes séparés en bons termes.
to be on bad terms with sb → être en mauvais termes avec qn
on equal terms [compete] → d'égal à égal
on the same terms → dans les mêmes conditions
to be on good terms with sb → être en bons termes avec qn
We parted on good terms → Nous nous sommes séparés en bons termes.
to be on bad terms with sb → être en mauvais termes avec qn
on equal terms [compete] → d'égal à égal
on the same terms → dans les mêmes conditions
to come to terms with sth [+ problem, situation] → faire face à qch; [+ sb's death] → accepter qch
in terms of sth (= as regards) → en ce qui concerne qch, pour ce qui est de qch
in terms of the climate → pour ce qui est du climat, en ce qui concerne le climat
in economic terms → du point de vue financier
Life is going to be a little easier in economic terms → La vie va être un peu plus facile du point de vue financier.
to think in terms of doing sth → penser à faire qch
in terms of the climate → pour ce qui est du climat, en ce qui concerne le climat
in economic terms → du point de vue financier
Life is going to be a little easier in economic terms → La vie va être un peu plus facile du point de vue financier.
to think in terms of doing sth → penser à faire qch
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
term
n
(= period of time) → Dauer f, → Zeitraum m; (of contract) → Laufzeit f; (= limit) → Frist f; term of government → Regierungszeit f; term of office → Amtsdauer or -zeit f; term of imprisonment → Gefängnisstrafe f; term of service (Mil) → Militärdienstzeit f; to set a term (of three years) for something → etw (auf drei Jahre) befristen; elected for a three-year term → auf or für drei Jahre gewählt; the contract is nearing its term → der Vertrag läuft bald ab; in the long/short term → auf lange/kurze Sicht; at term (Fin) → bei Fälligkeit; (Med) → zur rechten Zeit; to carry a baby to term → ein Kind (voll) austragen
(Sch, three in one year) → Trimester nt; (four in one year) → Vierteljahr nt, → Quartal nt; (two in one year) → Halbjahr nt; (Univ) → Semester nt; end-of-term exam → Examen nt → am Ende eines Trimesters etc; during or in term(-time) → während der Schulzeit; (Univ) → während des Semesters; out of term(-time) → in den Ferien
(= expression) → Ausdruck m; in simple terms → in einfachen Worten; a legal term → ein juristischer (Fach)ausdruck or Terminus (geh); he spoke of her in the most flattering terms → er äußerte sich sehr schmeichelhaft über sie; a contradiction in terms → ein Widerspruch in sich
(Math, Logic) → Term m; term in parentheses → Klammerausdruck m; to express one thing in terms of another → eine Sache mit einer anderen erklären; in terms of production we are doing well → was die Produktion betrifft, stehen wir gut da; in terms of money → geldlich, finanziell; in terms of time → zeitlich
terms pl (= conditions) → Bedingungen pl; terms of surrender/service/sale/payment → Kapitulations-/Arbeits-/Verkaufs-/Zahlungsbedingungen pl; terms of reference (of committee etc) → Aufgabenbereich m; (of thesis etc) → Themenbereich m; to buy something on credit/easy terms → etw auf Kredit/auf Raten kaufen; the hotel offered reduced terms in winter → das Hotel bot ermäßigte Winterpreise an; on what terms? → zu welchen Bedingungen?; not on any terms → unter gar keinen Umständen; to accept somebody on his/her own terms → jdn nehmen, wie er/sie ist; on equal terms → auf gleicher Basis; to come to terms (with somebody) → sich (mit jdm) einigen; to come to terms with something → sich mit etw abfinden
terms pl (= relations) to be on good/bad terms with somebody → gut/nicht (gut) mit jdm auskommen; to be on friendly terms with somebody → auf freundschaftlichem Fuß mit jdm stehen; they are not on speaking terms → sie reden nicht miteinander; what sort of terms are they on? → wie ist ihre Beziehung?
vt → nennen, bezeichnen
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007
term
[tɜːm]1. n
a. (limit) → termine m; (period) → periodo
in the short term → a breve scadenza
in the long term → a lungo andare
during his term of office → durante il suo incarico
term of imprisonment → periodo di detenzione or prigionia
to serve a 3-year term of imprisonment → scontare 3 anni di carcere
in the short term → a breve scadenza
in the long term → a lungo andare
during his term of office → durante il suo incarico
term of imprisonment → periodo di detenzione or prigionia
to serve a 3-year term of imprisonment → scontare 3 anni di carcere
b. (Scol) → trimestre m (Law) → sessione f
the autumn/spring/summer term → il primo/secondo/terzo trimestre
the autumn/spring/summer term → il primo/secondo/terzo trimestre
c. (word, expression) → termine m, vocabolo
to tell sb sth in no uncertain terms → dire qc chiaro e tondo a qn, dire qc a qn senza mezzi termini
in terms of ... → in termini di...
to tell sb sth in no uncertain terms → dire qc chiaro e tondo a qn, dire qc a qn senza mezzi termini
in terms of ... → in termini di...
d. terms npl (conditions) → condizioni fpl (Comm) → prezzi mpl, tariffe fpl
terms of employment → condizioni di impiego
terms of reference → termini mpl (stabiliti)
"easy terms" (Comm) → "facilitazioni di pagamento"
reduced terms for pensioners → agevolazioni fpl per i pensionati
on one's own terms → a modo proprio
to come to terms with (person) → arrivare a un accordo con (problem) → affrontare
to come to terms with a situation → accettare una situazione
not on any terms → a nessuna condizione
terms of employment → condizioni di impiego
terms of reference → termini mpl (stabiliti)
"easy terms" (Comm) → "facilitazioni di pagamento"
reduced terms for pensioners → agevolazioni fpl per i pensionati
on one's own terms → a modo proprio
to come to terms with (person) → arrivare a un accordo con (problem) → affrontare
to come to terms with a situation → accettare una situazione
not on any terms → a nessuna condizione
e. terms npl (relations) to be on good terms with → avere buoni rapporti con
not to be on speaking terms with sb → non rivolgere la parola a qc
not to be on speaking terms with sb → non rivolgere la parola a qc
2. vt (name) → definire
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995
term
(təːm) noun1. a (usually limited) period of time. a term of imprisonment; a term of office.
2. a division of a school or university year. the autumn term.
3. a word or expression. Myopia is a medical term for short-sightedness.
terms noun plural1. the rules or conditions of an agreement or bargain. They had a meeting to arrange terms for an agreement.
2. fixed charges (for work, service etc). The firms sent us a list of their terms.
3. a relationship between people. They are on bad/friendly terms.
verb to name or call. That kind of painting is termed `abstract'.
come to terms1. to reach an agreement or understanding. They came to terms with the enemy.
2. to find a way of living with or tolerating (some personal trouble or difficulty). He managed to come to terms with his illness.
in terms of using as a means of expression, a means of assessing value etc. He thought of everything in terms of money.
Kernerman English Multilingual Dictionary © 2006-2013 K Dictionaries Ltd.
term
→ تَعْبِير, فَصْلٌ دِرَاسِيّ pololetí, výraz betegnelse, semester Bezeichnung, Semester όρος, χρονική περίοδος término, trimestre lukukausi, termi terme, trimestre polugodište, termin termine, trimestre 学期, 用語 용어, 학기 term, termijn betegnelse, termin semestr, zwrot período, termo семестр, термин termin, villkor ภาคเรียน, ระยะเวลาที่กำหนด dönem, terim học kỳ, thuật ngữ 学期, 词语Multilingual Translator © HarperCollins Publishers 2009
term
n. término. período de tiempo de duración efectiva o limitada tal como en el embarazo;
vocablo.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
term
n (obst, etc.) término; at — a término; — pregnancy embarazo a términoEnglish-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.